Understanding Osteoporosis: A Growing Concern
As our lives extend, so do the challenges we face regarding health, particularly as we age. Osteoporosis, or "porous bones," is a condition that affects around 10 million people over the age of 50 in the United States. Alarmingly, an additional 45 million individuals have low bone mass, known as osteopenia, which can lead to osteoporosis. As Dr. Laila Tabatabai, a respected vice president of the Bone Health and Osteoporosis Foundation, highlights, being proactive about bone health is crucial as demographic trends signal an increasing number of individuals at risk for fractures and bone health issues.
When Should You Get Screened?
The importance of early screening cannot be overstated. The U.S. Preventive Services Task Force suggests that women at age 65 and younger women at increased risk should be screened for bone density. This contrasts with more inclusive recommendations from the Bone Health and Osteoporosis Foundation, advocating for comprehensive screening. Their approach encourages screening for not just older adults but also for those aged 50 and over who have experienced fractures or present other risk factors like family history, a smoking habit, or frequent falls.
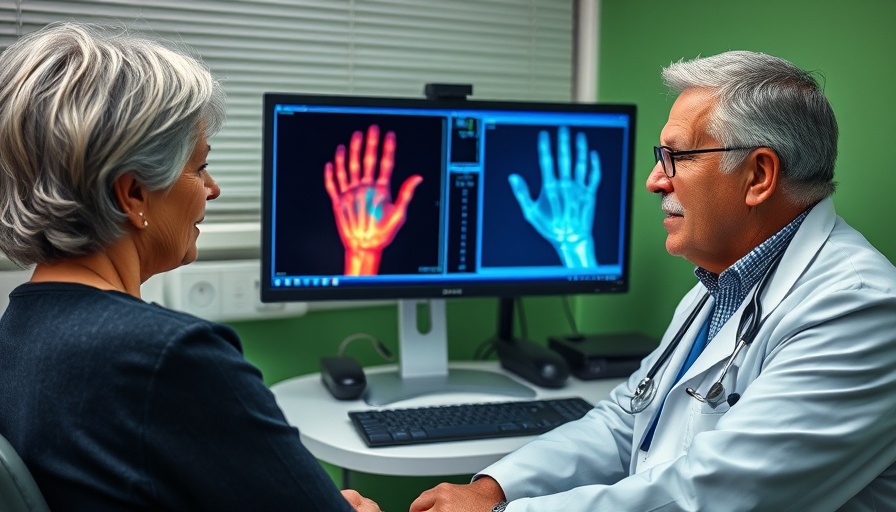
The Bone Density Test: What to Expect
A bone density test is a straightforward but informative procedure that provides insight into an individual's bone health. The test yields a T-score and a Z-score. The T-score compares your bone density against what is expected for a young healthy adult, while the Z-score compares your result with others of the same age and sex, highlighting whether your bone mass is lower than average for your demographic. A T-score greater than -1.0 is normal, while scores of -1.1 to -2.4 indicate low bone mass, and -2.5 or below is classified as osteoporosis.
Nourishing Your Bone Health
Bolstering your bone health requires a multifaceted approach that encompasses diet, lifestyle choices, and possibly supplementation. Dr. Tabatabai stresses the critical importance of calcium, recommending between 1,000 to 1,200 mg daily, predominantly from dietary sources to prevent complications related to high supplement intake. Foods rich in calcium, such as dairy products, leafy greens, and fortified items, not only bolster bone health but are associated with lower risks of kidney stones compared to supplements.
Vitamin D: A Hidden Hero
Coupled with calcium, Vitamin D plays an indispensable role in bone health. Achieving optimal Vitamin D levels, ideally between 40-60 nanograms per milliliter, facilitates calcium absorption and bone mineralization. Regular testing of 25-hydroxyvitamin D levels can help you assess whether you fall within this ideal range. Proper hydration also plays a protective role against kidney stones, a risk sometimes posed by excessive calcium supplementation. Therefore, staying well-hydrated with non-caffeinated beverages is essential for everyone, especially for those with a history of kidney stones.
Future-Proofing Your Bones: Steps You Can Take
Understanding the significance of proactive bone health cannot be overlooked. Taking preventive measures by scheduling routine screenings, adjusting your diet to prioritize calcium and vitamin D intake, and making lifestyle modifications can make the difference in preserving your bone health as you age. Such actions not only stave off osteoporosis but also positively impact your overall health and quality of life.
The Bottom Line: Empower Yourself with Knowledge
Bone health should be an integral part of health literacy, particularly for those nearing or past middle age. By acknowledging the risks and actively engaging in preventive strategies, individuals can ensure stronger bones as they progress through life. Regular check-ups and an informed lifestyle can facilitate independence and well-being well into the later years. Prioritize your bone health today by understanding your risk factors and assessing your nutritional needs.
If you're concerned about your bone health, consider discussing with a healthcare provider about appropriate screening measures and nutritional strategies tailored to your needs. Taking these proactive steps today can lead to long-term positive outcomes.
 Add Row
Add Row  Add
Add 




 Add Row
Add Row  Add
Add 

Write A Comment